Cloud computing has revolutionized how businesses and individuals store, manage, and access data. However, with convenience comes responsibility. As more sensitive information moves online, the importance of cloud security cannot be overstated.
Every year, cybercriminals find new ways to exploit vulnerabilities, and even small misconfigurations can lead to catastrophic breaches. Therefore, understanding cloud security and taking proactive measures is crucial.
Notably, cloud security involves protecting data, applications, and infrastructure hosted by cloud providers. Unlike traditional IT security, it requires knowledge of shared responsibilities, encryption methods, and continuous monitoring. Consequently, users must combine best practices with technological solutions to safeguard their assets.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore actionable cloud security tips, highlight potential risks, and provide expert strategies to ensure your cloud environment remains secure, compliant, and resilient against evolving threats.
Understanding Cloud Security
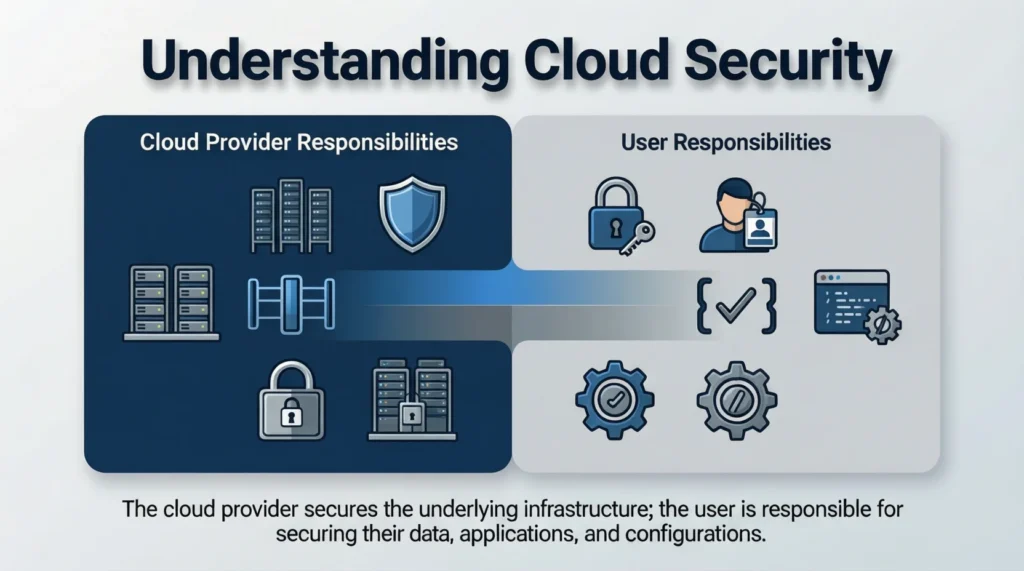
Before diving into tips, it is essential to understand what cloud security really entails. Essentially, cloud security is a collection of policies, technologies, and controls designed to protect data, applications, and services in cloud environments. Unlike traditional on-premise security, cloud security requires shared responsibility between the provider and the user.
Specifically, cloud providers manage the infrastructure, physical servers, and network security, whereas users are responsible for configuring access controls, managing permissions, and safeguarding data. Ignoring this shared responsibility model can lead to severe consequences, including data breaches, ransomware attacks, and loss of intellectual property. Moreover, regulatory compliance, such as GDPR or HIPAA, adds another layer of complexity, making cloud security a necessity rather than an option.
Key Cloud Security Challenges
Even though cloud computing offers many benefits, it also presents unique challenges:
- Data Breaches and Loss – Sensitive data stored in the cloud can become vulnerable to hacking, phishing, or insider threats. Without strong encryption and access management, confidential information can be compromised.
- Misconfigured Cloud Settings – Surprisingly, many cloud security issues arise from simple misconfigurations, such as open storage buckets or weak passwords.
- Unauthorized Access – Improper access management can allow hackers or malicious insiders to manipulate or steal information.
- Compliance Risks – Organizations often struggle to meet strict data protection regulations in a complex cloud environment.
- Shared Responsibility Confusion – Many users mistakenly assume the cloud provider handles all security, leaving gaps that attackers can exploit.
Understanding these challenges helps prioritize measures that mitigate risk effectively.

Top Cloud Security Tips
To secure your cloud environment, consider these essential practices:
1. Implement Strong Identity and Access Management (IAM)
First and foremost, controlling who accesses your cloud resources is critical. Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security, and apply the principle of least privilege by granting only necessary permissions. Furthermore, regularly audit user accounts and remove inactive or unnecessary access.
2. Encrypt Data at Rest and in Transit
Encryption protects sensitive information from unauthorized access. Specifically, use provider-native encryption tools or third-party solutions for data storage. Additionally, ensure all data transmitted to and from the cloud uses SSL/TLS encryption. Consequently, even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable to attackers.
3. Regularly Backup Your Data
Backups are your safety net. Automate cloud backups and verify recovery processes to ensure minimal disruption in case of a breach or accidental deletion. Moreover, storing backups in multiple geographic regions adds redundancy and further protects against disaster scenarios.
4. Monitor and Audit Your Cloud Environment
Continuous monitoring detects anomalies before they escalate. Use cloud monitoring tools, enable logging, and review audit trails frequently. In doing so, you can spot suspicious activity, investigate incidents, and maintain compliance efficiently.
5. Keep Systems and Applications Updated
Unpatched software is a major vulnerability. Therefore, regularly apply security patches and updates to operating systems, applications, and APIs. This proactive approach significantly reduces the risk of exploits targeting known vulnerabilities.
6. Use Secure APIs
APIs connect cloud services but can be exploited if insecure. Always authenticate API calls, avoid exposing sensitive endpoints, and follow secure development practices. Consequently, your integrations remain safe from common attacks such as injection or brute force attempts.
7. Educate Employees and Establish Security Policies
Human error is one of the leading causes of cloud breaches. Implement training programs on phishing, password hygiene, and social engineering. Simultaneously, create clear policies that define how employees should access and manage cloud resources.
8. Leverage Advanced Threat Detection Tools
Modern security solutions, including AI and machine learning, help detect unusual activity in real-time. Tools like cloud-native Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems can alert administrators to potential threats immediately, enabling rapid response.
9. Evaluate Cloud Service Providers Carefully
Not all cloud providers offer the same security guarantees. Ensure your provider meets industry standards such as ISO 27001 or SOC 2, and understand your shared responsibility boundaries. Moreover, choose providers with robust compliance programs to simplify regulatory adherence.
Cloud Security Best Practices for Businesses
Businesses need to go beyond basic tips to build a resilient security posture:
- Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities.
- Classify data according to sensitivity, applying stricter controls to critical information.
- Develop incident response plans and simulate breaches to test readiness.
- Use network segmentation, secure VPNs, and private connections to limit exposure.
- Continuously review cloud configurations to avoid misconfigurations that attackers exploit.
By integrating these practices, organizations create a layered defense that reduces risk and ensures long-term cloud security.

Common Cloud Security Myths Debunked
It is also important to clear misconceptions that can undermine cloud security:
- “Cloud providers handle all security” – Providers secure the infrastructure, but users are responsible for data and access management.
- “Encryption alone is enough” – While essential, encryption must be paired with monitoring, access control, and secure configurations.
- “Small businesses don’t need advanced security” – Attackers often target smaller organizations assuming weaker defenses, making robust security critical regardless of size.
Future Trends in Cloud Security
Cloud security is constantly evolving. Notably, organizations are adopting zero-trust models, enforcing verification for every access attempt. AI-powered monitoring is increasingly common, helping detect sophisticated threats quickly. Cloud-native security tools and automation simplify protection and reduce manual errors. Furthermore, compliance and data privacy are gaining prominence, with new regulations emphasizing accountability for cloud users. Staying ahead of these trends ensures your environment remains safe and future-proof.
FAQs About Cloud Security
Q1: Is my cloud provider responsible for all security?
No. Cloud security follows a shared responsibility model: providers secure infrastructure, users secure data and access.
Q2: How often should I audit my cloud environment?
Ideally, conduct monthly audits and review logs continuously to detect anomalies.
Q3: What is the easiest way to encrypt cloud data?
Use built-in encryption tools from your cloud provider, such as AWS KMS, Azure Key Vault, or GCP Cloud KMS.
Q4: Can small businesses be targeted in the cloud?
Yes. Attackers often target smaller organizations due to perceived weaker defenses, making security essential for all.
Q5: What are the most common cloud security mistakes?
Misconfigurations, weak passwords, lack of MFA, and neglecting audits are the top causes of breaches.
Final Thought
In conclusion, cloud security is not a one time task but a continuous process. By implementing strong access controls, encrypting data, monitoring activity, and educating users, you can significantly reduce risk.
Moreover, staying informed about trends, using advanced tools, and understanding shared responsibility ensures your cloud environment remains resilient.
Ultimately, proactive cloud security empowers businesses and individuals to leverage cloud computing with confidence, knowing their data and applications are protected against evolving threats.

Naz Fatima is an author at Saypadia who specializes in writing clear, relatable, and reader-friendly content about language, expressions, and modern terminology. She enjoys breaking down meanings with real-life context so readers can quickly understand and apply them. Naz’s work reflects a strong commitment to clarity, accuracy, and helping users find quick answers without confusion.




