You might hear the word insulin at a doctor’s office, in a health video, or during a casual conversation about sugar or diabetes. Maybe someone said, “my insulin is low,” and you nodded, even though you weren’t fully sure what that meant.
That’s normal. Insulin sounds technical, but what it does is actually pretty simple. Once you understand it, a lot of things about energy, blood sugar, and health suddenly make sense. Let’s explain it in clear, everyday language no medical background needed.
Quick Answer:
Insulin is a hormone that helps move sugar from your blood into your cells so your body can use it for energy.
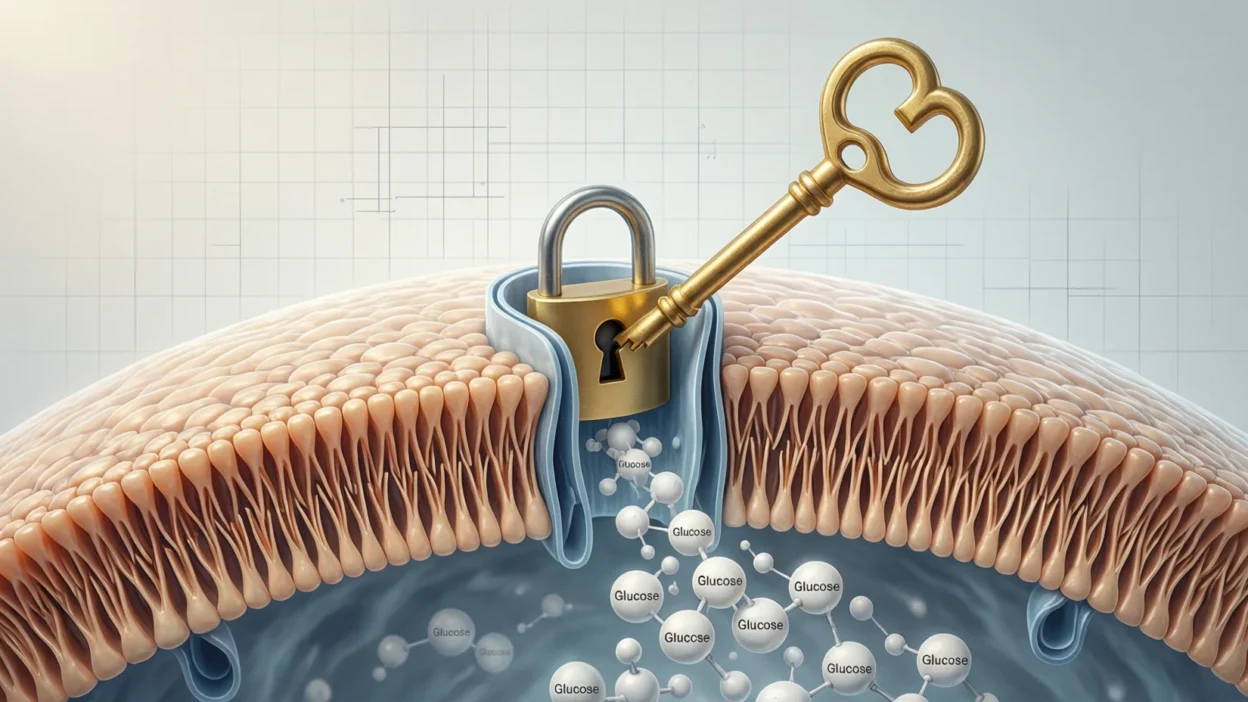
What Does Insulin Do in the Body?
Insulin acts like a key. It unlocks your body’s cells so sugar can enter and be used as fuel.
Plain-English Explanation
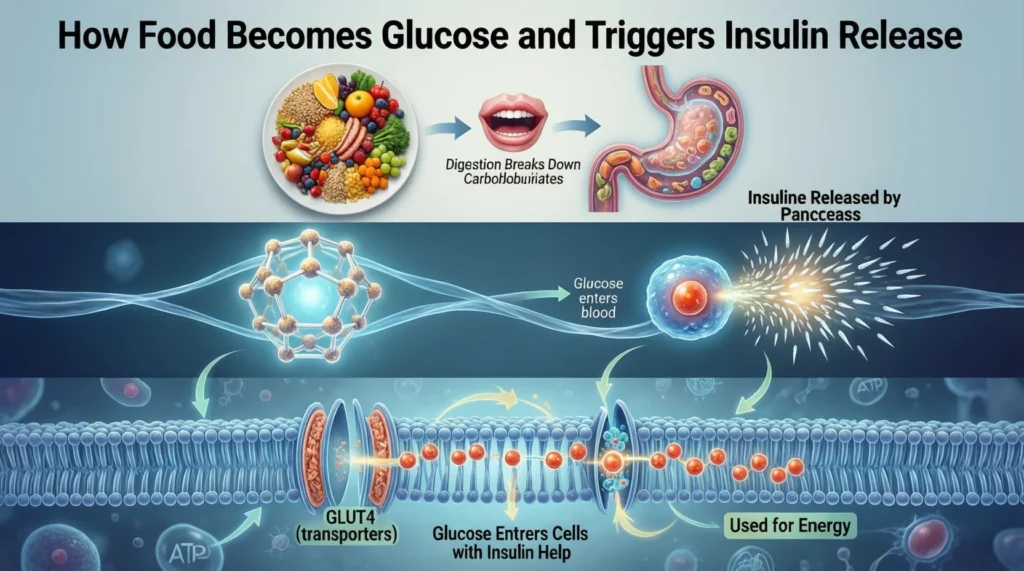
When you eat food, especially carbs like bread, rice, or fruit, your body breaks it down into glucose (a type of sugar). That sugar enters your bloodstream. Insulin’s job is to take that sugar out of the blood and push it into your cells, where it becomes energy.
Without insulin, sugar stays in the blood instead of helping your body work.
Example:
After eating lunch, insulin helps your body use the food for energy instead of letting sugar build up in your blood.
Bold Summary: Insulin helps control blood sugar by allowing sugar to enter your cells and be used for energy.
Where Does Insulin Come From?
Insulin is made by the pancreas, a small organ behind your stomach.
Here’s how it works:
- You eat food
- Blood sugar rises
- Pancreas releases insulin
- Insulin moves sugar into cells
- Blood sugar levels return to normal
This process happens many times every day without you noticing.
Why Is Insulin So Important?
Insulin is essential because it:
- Keeps blood sugar at healthy levels
- Gives your body energy
- Helps muscles grow and repair
- Supports brain function
- Prevents damage to organs
When insulin doesn’t work properly, the body struggles to function normally.
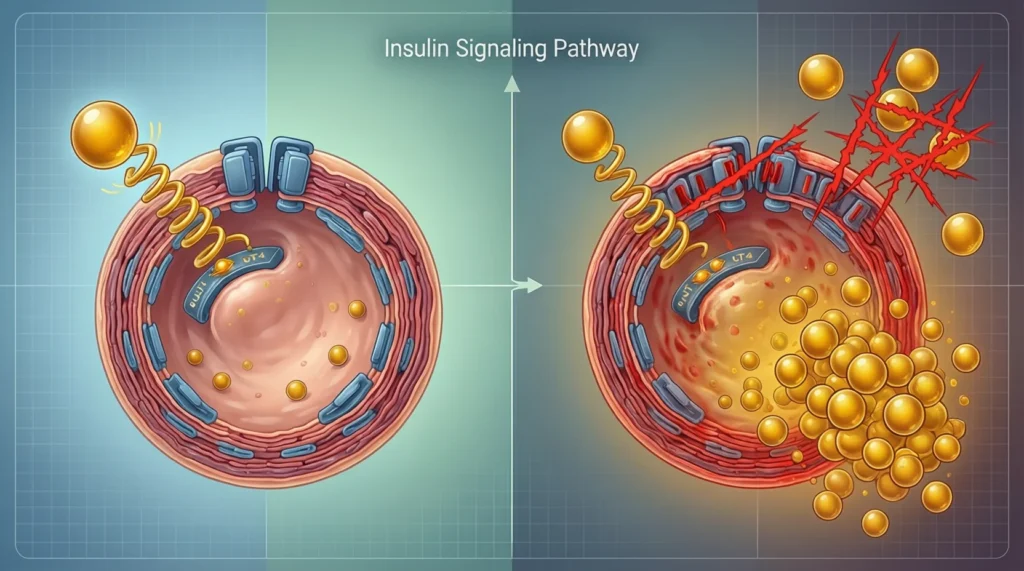
What Happens When Insulin Is Too Low or Doesn’t Work?
If insulin is missing or not working well, sugar builds up in the blood. This leads to health problems.
Low or Missing Insulin
- High blood sugar
- Extreme thirst
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue
- Blurry vision
Insulin Resistance
Sometimes the body makes insulin, but cells stop responding to it. This is called insulin resistance.
Over time, this can lead to:
- Type 2 diabetes
- Weight gain
- Heart problems
Insulin and Diabetes: The Connection
Insulin is closely linked to diabetes.
Type 1 Diabetes
- Body doesn’t make insulin
- Requires insulin injections
- Usually starts early in life
Type 2 Diabetes
- Body makes insulin but doesn’t use it well
- Often linked to lifestyle and genetics
- May or may not require insulin shots
Simple Comparison Table
| Type | Insulin Production | Main Issue |
|---|---|---|
| type 1 | none | insulin missing |
| type 2 | some | insulin resistance |
How Insulin Affects Energy and Mood
Insulin doesn’t just affect blood sugar—it affects how you feel.
When insulin works properly:
- You feel steady energy
- Less brain fog
- Better focus
When insulin is off:
- Energy crashes
- Mood swings
- Feeling tired after meals
That “sleepy after eating” feeling is often related to blood sugar changes.
Everyday Examples of Insulin at Work
Here’s how insulin shows up in daily life:
- After breakfast, insulin helps fuel your brain
- During exercise, insulin helps muscles use sugar
- After dinner, insulin stores extra sugar for later use
- Between meals, insulin levels drop so your body can use stored energy
Insulin quietly manages energy all day long.
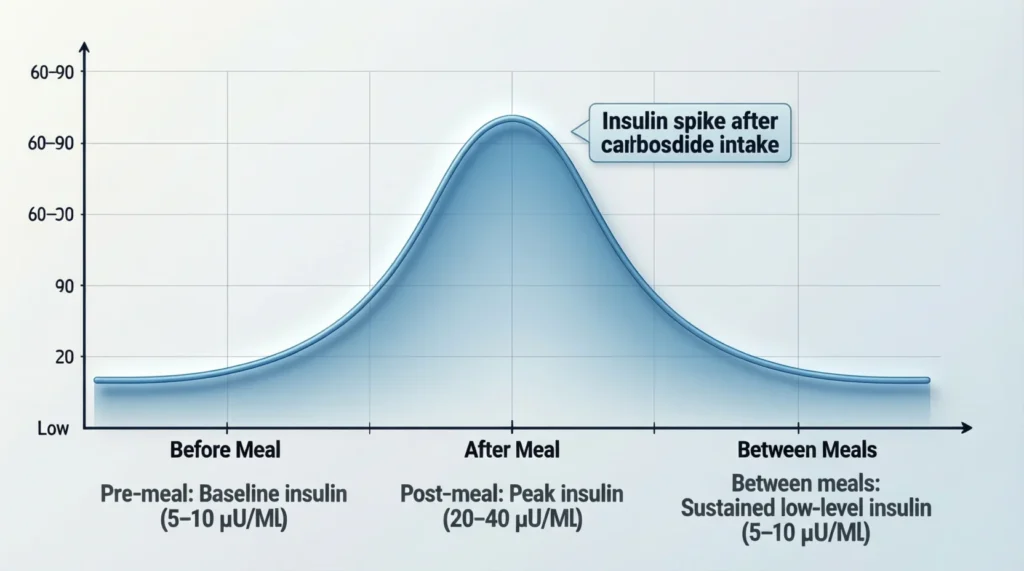
When Insulin Spikes and Drops
When Insulin Increases
- After eating carbs or sugar
- During stress
- After large meals
When Insulin Decreases
- Between meals
- During fasting
- Overnight
Balance is key. Too many spikes over time can cause problems.
When to Be Careful About Insulin
✅ Healthy Insulin Use
- Balanced meals
- Regular movement
- Proper sleep
- Stress management
❌ Problems Can Happen When
- Diet is very high in sugar
- Little physical activity
- Chronic stress
- Ignoring blood sugar issues
Context Table
| Situation | Insulin Effect | Why |
|---|---|---|
| balanced meal | steady insulin | healthy control |
| sugary snack | insulin spike | fast sugar rise |
| exercise | better insulin use | cells respond better |
| poor sleep | insulin resistance | body stress |
Common Myths About Insulin
- Myth: Insulin is only for diabetics
Truth: Everyone needs insulin - Myth: Insulin causes diabetes
Truth: Diabetes is caused by insulin problems, not insulin itself - Myth: Sugar alone controls insulin
Truth: Stress, sleep, and activity also matter
FAQs About “What Does Insulin Do?”
1. Is insulin a drug or hormone?
Insulin is a natural hormone made by the body.
2. Does everyone produce insulin?
Yes, except people with type 1 diabetes.
3. Can insulin levels change daily?
Yes, they change throughout the day.
4. Does insulin make you gain weight?
Insulin helps store energy, but balance matters.
5. Can lifestyle improve insulin function?
Yes, diet, exercise, and sleep help a lot.
6. Is insulin only related to sugar?
Mostly, but it also affects fat and protein use.
7. Why do doctors test insulin levels?
To understand blood sugar control and diabetes risk.
Final Thought
So, what does insulin do? It acts as your body’s energy manager, helping move sugar from your blood into your cells so you can think, move, and live normally.
Without insulin or when it doesn’t work well your body struggles to function. Understanding insulin makes it easier to understand energy, diabetes, and overall health in a simple, practical way.

Robat Hood is a creative writer and contributor at Saypadia, focused on explaining trending words, slang, and cultural phrases in a simple and engaging way. With a sharp eye for modern language trends, Robat aims to make Saypadia a trusted place for understanding how words are used online and in daily conversations. His content is informative, approachable, and designed for readers of all levels.